A Guest Post By Aaron Bostick, Deputy Chief Information Security Officer, ThriveDX
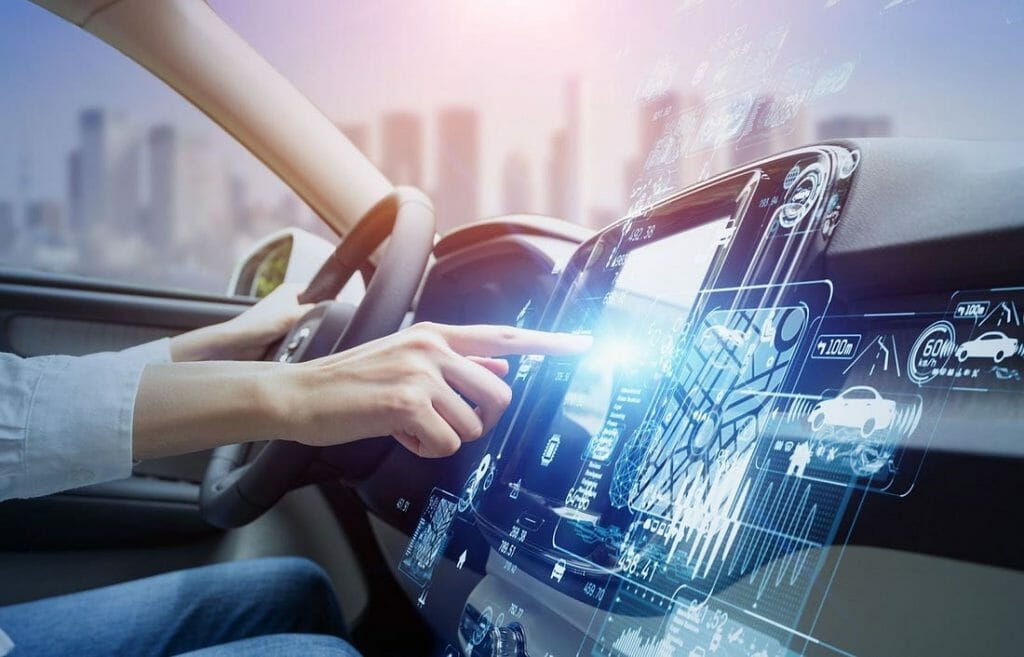
The pandemic altered so many aspects of life. A distracted world became the playground for cybercriminals. About 50% of all auto cyber attacks occurred in 2021 alone, marking a 140 percent increase from 2020, according to GovTech.
Cyber attacks cost the automotive industry $1.1 billion every year. This formidable challenge requires drastic security measures and risk-mitigating playbooks from cybersecurity experts.
Automakers plan to have millions of connected vehicles in 2024 and the decades to come.
The issue has become so prevalent, startups companies have noticed the widening gap in cybersecurity and have begun offering cloud-based automotive cybersecurity and data analytics platforms to protect:
- Over-the-air updates
- On-demand features
- Tech perks
Smart Mobility
About six percent of smart mobility providers were the target of cyber attacks in 2022, compared to just two percent in 2021. Cybercriminals can take control of vehicle functions and gain access to the greater electric grid. Researchers demonstrated the vulnerability of smart cars to cyber attacks from remote locations by disabling brakes, operating the steering wheel and shutting down the engine.
Privacy infringement and identity theft
Internet-enabled cars desperately need cybersecurity to keep drivers and passengers safe, especially as technology advances every year. Privacy infringement and identity theft in cars are two major concerns with automotive hacking. Cyber criminals infiltrate data centers and back-end servers to steal personal data. More than 40 percent of all auto cybersecurity issues directly or indirectly relate to back-end application servers.
Cyber Risks
A single attack can cost an automaker up to $1 billion dollars. Cyber risk is shared by fleet operators, tier 1 suppliers and car-sharing companies. The entire automotive industry could potentially face losses of up to $24 billion in 2023.
Vehicles have become just another connected device to cybercriminals. Because they are always-on devices, there are now a wealth of cybersecurity concerns:
- Car hijacking
- Malicious data breaches
- Use of unsecured wireless networks
- Organized attacks
- Software vulnerabilities
Each of these potential risks pose a threat to the safety and integrity of the vehicles, as well as to private information stored within them.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a powerful attack tool given the recent advancements toward driverless cars. User data is an attractive target for cybercriminals who want to steal Personally Identifiable Information (PII) such as credit card information, home addresses, and even email addresses. Cybercriminals craft convincing phishing emails with malicious links to gain access to the victims’ personal devices, including their vehicles where data can be held for ransom.
Data Protection Approach
Automakers need to upgrade their data protection methodologies to stay ahead of cybercriminals. Perimeter security and intrusion detection are just the basics now. Tokenization and other encrypted methods need to be explored for customer privacy and operational safety.
Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
With the integration of technology in the auto industry, there needs to be a securer, safer way to protect cars from external attacks. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) safeguard a car’s engine control and electronics systems. Users can simultaneously access the internet securely from their vehicle. Some are using their car-based VPNs to safely access co-working spaces or company networks.
Infrastructure
Critical infrastructure should be taken very seriously not only by the car companies and the fleet owners but also by the government. Cybercriminals want private information, including credit card numbers, digital keys to unlock and start vehicles to be stolen, and access to electric-vehicle charging stations for installing ransomware.
Cyber Warfare
Shutting down public charging stations is a means of cyber warfare. Attacks can disrupt critical systems and infrastructure, as charging stations are essential to keeping many technologies operational. These highly targeted threats range from disabling electric vehicles to disrupting supply chains, deliveries and other services.
The worst-case scenario is a region being shut down via the greater electric grid. Depending on the type of attack, some protective measures are automatic, while others may take longer to put in place. Actions may also include disabling the SIM card in a vehicle, working with the automaker’s cybersecurity team and contacting the driver to notify them of the attack.
Auto Cybersecurity
Automakers are increasingly turning to cybersecurity experts thanks to unprecedented threats moving faster than anyone predicted. Automakers must respond with equal speed and accuracy to protect their brand and the greater electric grid. Cybersecurity professionals are uniquely adept at detecting potential risks and determining the best course of action. Their superior understanding of cyber threats allows them to quickly develop playbooks and mitigate risks in close to real-time.
Fully staffed automotive manufacturers and insurance companies can rest assured knowing they have a team of experts protecting them against malicious cyber activities.
The Future of Auto Cybersecurity
Automakers must focus on cybersecurity as a key aspect of their vehicles’ AI features when designing, building, and deploying those cars. Effective security measures need to be woven into the development process from the beginning to deter malicious cyberattacks. Skimping on security measures at any point will leave drivers vulnerable to potential threats, including malicious hacking and data breaches.
Automakers can avoid devastating data losses and cybersecurity incidents that could lead to regulatory action, customer losses, and reputation damage. Taking an active role in securing vehicles is essential for car manufacturers to remain innovative and competitive in an ever-evolving automotive landscape.
The automotive world has realized it needs to stay up to date with technology, especially when it comes to cybersecurity. On that note, it’s important to keep your technical employees’ cyber skills sharp with advanced training and specialized courses. To level-up your organization’s cyber threat awareness and preparedness with custom-fit training content, visit https://thrivedx.com/.