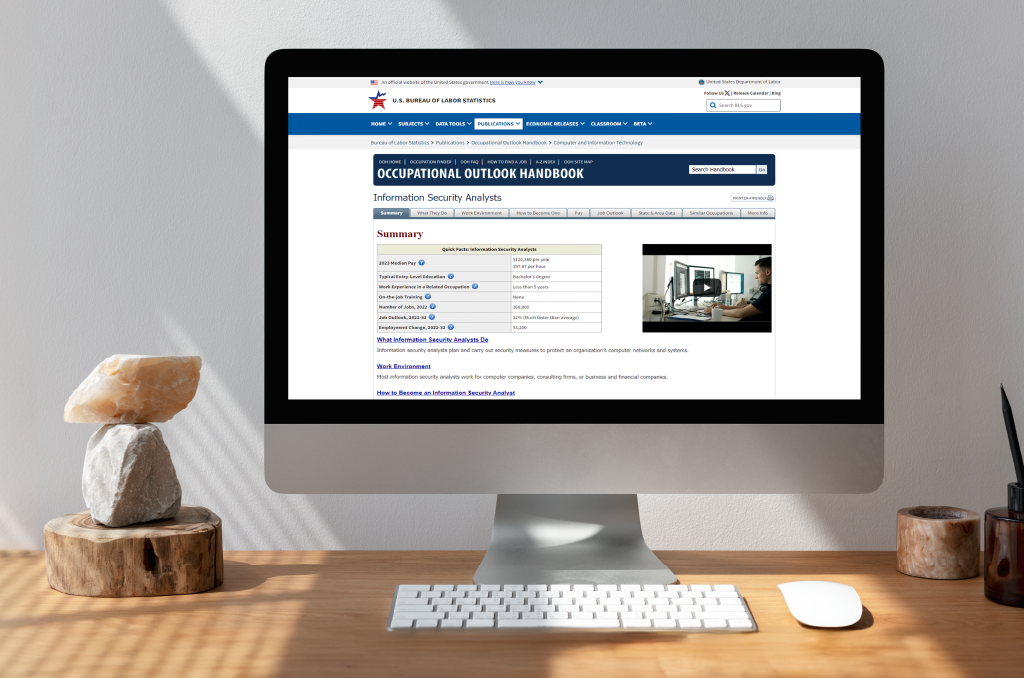
The need for cybersecurity professionals is experiencing unprecedented growth, with the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projecting a 32% growth rate for information security analysts from 2018 to 2028. The increasing need to protect organizations from cyber threats drives this above-average growth rate.
Cybersecurity certifications are crucial in meeting this demand by bridging the skills gap. These certifications validate individuals’ skills and knowledge, ensuring they are equipped to safeguard data and systems effectively.
Cybersecurity certifications are designed to test and confirm an individual’s expertise in various aspects of cybersecurity. They provide a structured pathway for professionals to gain and demonstrate proficiency in network security, ethical hacking, risk management, and compliance. By obtaining certifications, professionals can showcase their commitment to staying current with the latest cybersecurity trends, technologies, and best practices, making them valuable assets to any organization.
Why Pursue Cybersecurity Certifications?
Pursuing certifications in IT security offers several key benefits. Certifications for cybersecurity enhance job prospects by making you a more attractive candidate to employers, showing that you have specialized skills. They often lead to higher earning potential, with certified professionals commanding higher salaries than their non-certified peers.
Certifications in cybersecurity open doors to advanced positions and leadership roles, facilitating career advancement. Additionally, certifications help you stay current with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices in the constantly evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Certifications in cybersecurity also validate your technical abilities and managerial skills, making you eligible for roles such as security analyst, IT auditor, security manager, and CISO. Certifications also help you stay current with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices in the constantly evolving cybersecurity landscape, ensuring your skills remain relevant and effective in combating emerging threats.

Boosting Your Employability
Pursuing certifications in IT security significantly enhances your resume and makes you stand out to potential employers. Cybersecurity certifications, like CISSP and CEH, demonstrate your commitment to the field and validate your skills and knowledge in handling cybersecurity challenges.
Research shows that 93% of employers find certifications beneficial for ensuring their IT staff is knowledgeable and up-to-date. Certified professionals often have better job prospects and a higher chance of landing interviews than non-certified candidates.
Certifications in cybersecurity also lead to higher salaries and career advancement opportunities. Certified cybersecurity professionals often command higher salaries than their non-certified peers, making certifications a valuable investment. These credentials can serve as stepping stones to more senior roles within organizations. With the ongoing surge in cyberattacks, the demand for skilled cybersecurity experts grows, making cybersecurity certifications even more valuable. For beginners, starting with the best cybersecurity certifications can lay a strong foundation for a successful career in this dynamic field.
By pursuing the best cybersecurity certifications, you can build a strong foundation for a successful and rewarding career in cybersecurity.

Validating Your Skills
Cybersecurity certifications are essential for establishing professional credibility and expertise in the field. They formally acknowledge that an individual has acquired the necessary skills to effectively protect and manage digital assets.
For instance, the Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) certification offered by ISACA focuses on cybersecurity management and governance, highlighting an individual’s ability to manage and assess an enterprise’s information security program. According to a study by ISACA, 87% of professionals view credential-holders as the most qualified for open positions, and 74% are more likely to hire a Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) certification over a non-certified candidate.
Moreover, the Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP) certification emphasizes practical, hands-on skills in penetration testing, proving an individual’s capability to identify and exploit vulnerabilities. Data from the International Information System Security Certification Consortium (ISC2) suggests that professionals with advanced certifications like CISSP can earn up to 25% more than their uncertified peers. These certifications not only enhance job prospects but also pave the way for career advancement and higher earning potential, making them a critical investment for anyone serious about a career in cybersecurity.

Learn CompTIAⓇ Security+
The CompTIAⓇ Security+ certification is a globally recognized credential that validates foundational skills in cybersecurity. It is an ideal entry-level certification for individuals starting their careers in this field.
Eligibility Criteria and Key Topics Covered
To earn the CompTIAⓇ Security+ certification, no prerequisites are required, but having at least two years of IT experience with a focus on security is recommended. The certification exam covers critical topics, including understanding and mitigating security threats, knowledge of security technologies and tools, designing secure network architectures, managing identity and access, risk management, and understanding cryptography and PKI.
Where Can You Learn CompTIAⓇ Security+?
Numerous resources are available for learning CompTIAⓇ Security+, including online courses, study guides, and boot camps. Popular platforms include the official CompTIAⓇ resources, LinkedIn Learning, online learning programs like the ThriveDX Cybersecurity Impact Bootcamp, and many community colleges and universities offering focused training programs.

CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) Certification
The Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) certification is a globally recognized credential offered by ISACA for professionals who audit, control, monitor, and assess an organization’s IT and business systems. To earn the CISA certification, candidates need at least five years of professional experience in information systems auditing, control, or security. However, up to three years of this requirement can be substituted with specific education or other certifications.
The CISA exam contains 150 multiple-choice questions covering five key domains: Information System Auditing Process, Governance and Management of IT, Information Systems Acquisition, Development, and Implementation, Information Systems Operations and Business Resilience, and Protection of Information Assets.
The CISA certification validates an individual’s expertise in auditing and securing information systems, confirming their ability to assess vulnerabilities, report on compliance, and institute controls within an enterprise. Employers highly value this certification–it can lead to enhanced job prospects, higher salaries, and career advancement opportunities, including senior and leadership roles in IT auditing and security. Recognized worldwide, the CISA certification provides career advancement opportunities across different countries and industries.
CISSP
The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification, offered by ISC2, is a globally recognized credential for professionals in information security. Designed for those who aim to demonstrate their expertise in designing, implementing, and managing a best-in-class cybersecurity program, the CISSP is highly regarded in the industry.
To earn the CISSP certification, candidates need at least five years of cumulative, paid work experience in at least two of the eight CISSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK) domains. These domains include Security and Risk Management, Asset Security, Security Architecture and Engineering, Communication and Network Security, Identity and Access Management (IAM), Security Assessment and Testing, Security Operations, and Software Development Security. One year of experience can be waived with a four-year college degree or an approved credential.
The CISSP certification validates an individual’s deep technical and managerial knowledge, ensuring they are equipped to effectively design, engineer, and manage the overall security posture of an organization. This certification significantly enhances job prospects, making professionals more competitive candidates for senior and leadership roles in cybersecurity.
Certified CISSP professionals often earn higher salaries compared to their non-certified peers and enjoy opportunities for career advancement and higher-level positions within the field. Recognized worldwide, the CISSP certification provides various career opportunities across different industries and regions.

AWS Certified Security
The AWS Certified Security – Specialty certification is a valuable credential for professionals specializing in securing the Amazon Web Services (AWS) platform. Designed for individuals with at least two years of hands-on experience in securing AWS workloads, this certification validates an individual’s ability to implement effective security practices in the AWS environment.
Candidates should have a minimum of five years of IT security experience, including at least two years with AWS security services. The certification exam covers key topics such as incident response, logging and monitoring, infrastructure security, identity and access management, and data protection.
Earning the AWS Certified Security – Specialty certification demonstrates an individual’s expertise in securing data and workloads on the AWS platform, ensuring they have the necessary skills to design and implement robust security solutions. This certification significantly enhances job prospects by showcasing specialized skills in AWS security, making professionals more competitive candidates for roles in cloud security. Certified individuals often enjoy higher earning potential and opportunities for career growth and advancement in cloud security.

CISM (Certified Information Security Manager)
The Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) certification, offered by ISACA, is a globally recognized credential for professionals who manage, design, oversee, and assess an enterprise’s information security.
Focusing on the managerial aspects of information security, including risk management, governance, and incident response, the CISM certification requires candidates to have at least five years of professional experience in information security management, with at least three years in three or more of the CISM content areas. These areas include Information Security Governance, Information Risk Management, Information Security Program Development and Management, and Information Security Incident Management. Candidates must also pass the CISM exam covering these critical topics.
The CISM certification validates an individual’s expertise in aligning information security with broader business goals and objectives. It enhances job prospects by showcasing specialized skills in information security management, making certified professionals more competitive for senior and leadership roles. Additionally, CISM-certified individuals enjoy higher earning potential and more significant career advancement opportunities.

CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker)
The Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) certification, offered by the EC-Council, is a globally recognized credential for professionals specializing in ethical hacking and penetration testing. To earn the CEH certification, candidates need at least two years of work experience in information security or attend an official EC-Council training. The CEH exam covers ethical hacking principles, footprinting, network scanning, enumeration, system hacking, malware threats, sniffing, social engineering, DoS attacks, session hijacking, web server and application hacking, SQL injection, wireless network hacking, and cryptography.
The CEH certification validates a professional’s ability to identify and fix security vulnerabilities using the same tools and techniques as malicious hackers but in a lawful manner. This certification enhances job prospects, as it is highly valued by employers looking for skilled, ethical hackers. It often leads to higher earning potential and career advancement opportunities. The certification is recognized globally, providing flexibility and growth across different industries.

OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional)
The Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP) certification is a highly respected credential for professionals in ethical hacking and penetration testing, offered by Offensive Security. The OSCP certification focuses on practical, hands-on skills in identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities. Candidates must complete the Offensive Security Penetration Testing with Kali Linux (PWK) course and pass a rigorous 24-hour hands-on exam that tests their ability to compromise various machines in a controlled environment.
The OSCP certification has no formal prerequisites, but candidates must understand networking, Linux, and basic programming concepts. Key topics covered in the PWK course and exam include network scanning, enumeration, exploitation, buffer overflows, privilege escalation, client-side attacks, web application attacks, and post-exploitation techniques.
The OSCP certification validates a professional’s ability to perform advanced penetration testing and security assessments. It demonstrates proficiency in using various hacking tools and techniques to identify and mitigate security risks.
The OSCP certification enhances job prospects, often leading to higher earning potential and career advancement in cybersecurity roles. The certification is globally recognized and highly regarded by employers, making it a valuable asset for professionals seeking to establish or advance their careers in ethical hacking and penetration testing.
Earning Higher Salaries
Earning cybersecurity certifications offers numerous career benefits, including enhanced job prospects, higher earning potential, and opportunities for career advancement. Here are some potential salary increases associated with specific certifications:
CISSP: Professionals with CISSP certification can see 20% or more salary increases, with average salaries often exceeding $120,000 annually.
CEH: Certified Ethical Hackers can expect a salary increase of 10% to 15%, with average salaries ranging from $70,000 to $100,000.
CISM: CISM holders often experience a salary increase of around 15% to 20%, with average salaries around $110,000.
OSCP: OSCP-certified professionals can see salary increases ranging from 10% to 25%, depending on their role and experience, with salaries often exceeding $90,000.
CompTIAⓇ Security+: As an entry-level certification, Security+ can boost salaries by 5% to 10%, with average earnings between $60,000 and $80,000.
Conclusion:
Pursuing certifications in IT security offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance your career. These certifications validate your skills and knowledge, making you a more attractive candidate to potential employers. Certifications for cybersecurity demonstrate your commitment to the field and ensure you stay current with the latest cybersecurity trends and technologies. Certifications such as CISSP, CEH, CISM, OSCP, and CompTIAⓇ Security+ are highly regarded in the industry and can lead to substantial salary increases, improved job prospects, and opportunities for career advancement.
Earning cybersecurity certifications provides industry-recognized validation of your technical abilities and expertise, opening doors to advanced roles and leadership positions. Certified professionals are often better equipped to protect organizations from cyber threats, making them invaluable assets to any team. Whether you are looking for the best cybersecurity certifications or cybersecurity certifications for beginners, now is the perfect time to embark on your cybersecurity journey. Use this comprehensive guide to choose the right certifications for your career goals.

FAQ
What is the importance of cybersecurity certifications?
Cybersecurity certifications are essential because they validate an individual’s skills and knowledge in the field, making them more attractive to potential employers. They demonstrate a commitment to staying current with industry standards and best practices, and they often lead to higher salaries and career advancement opportunities. Certifications help bridge the skills gap in the cybersecurity workforce, ensuring that professionals are equipped to protect organizations from cyber threats.
How do cybersecurity certifications enhance skills?
Cybersecurity certifications enhance skills by providing structured learning paths and comprehensive training in specific areas of cybersecurity. They cover a wide range of topics, from ethical hacking and penetration testing to risk management and security operations. By preparing for certification exams, professionals gain practical knowledge and hands-on experience with the latest tools and technologies, which improves their ability to address real-world security challenges.
Are there prerequisites for cybersecurity certifications?
Many cybersecurity certifications have prerequisites, but they vary by certification. For example, the CISSP requires five years of work experience in at least two of its eight domains, while the CEH requires two years of work experience in information security. Some entry-level certifications, such as CompTIAⓇ Security+, do not have formal prerequisites but recommend certain levels of knowledge or experience.
How long is the typical duration of a cybersecurity certification program?
The duration of a cybersecurity certification program varies depending on the certification and the individual’s prior knowledge and experience. On average, preparing for a certification can take anywhere from a few months to a year. For example, the CISSP typically requires extensive study over several months, while the CEH and CompTIA Security+ may take a shorter time to prepare for if the candidate has relevant experience.
What types of cybersecurity certifications are available?
There are numerous types of cybersecurity certifications available, each catering to different specializations and career paths. Some of the most popular certifications include:
CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional)
CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker)
CISM (Certified Information Security Manager)
OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional)
CompTIAⓇ Security+
How often should cybersecurity certifications be renewed?
The renewal period for cybersecurity certifications varies. For example, the CISSP must be renewed every three years through continuing professional education (CPE) credits, while the CEH requires renewal every three years either by earning CPE credits or retaking the exam. It’s important to check the specific renewal requirements for each certification.
Can cybersecurity certifications be earned online?
Yes, many cybersecurity certifications can be earned online. Training programs, study materials, and exams are often available in online formats, making it convenient for professionals to prepare and obtain their certifications remotely. Organizations like CompTIA, EC-Council, and ISC2 offer online options for their certification programs.
Do certifications focus on specific cybersecurity domains?
Yes, cybersecurity certifications often focus on specific domains or areas of expertise. For example:
CISSP covers eight domains, including security and risk management, asset security, and software development security.
CEH focuses on ethical hacking techniques and tools.
CISM emphasizes information security management, governance, and risk management.
OSCP focuses on hands-on offensive security skills and penetration testing.
What are the common exam formats for cybersecurity certifications?
The exam formats for cybersecurity certifications vary but generally include multiple-choice questions, scenario-based questions, and practical exams. For example, the CISSP exam consists of multiple-choice questions, while the OSCP exam includes a 24-hour hands-on practical test where candidates must exploit vulnerabilities in a controlled environment.
Are there study materials available for cybersecurity certifications?
Yes, there are extensive study materials available for cybersecurity certifications. These include official study guides, online courses, practice exams, video tutorials, and instructor-led training. Certification vendors and various online platforms provide these resources to help candidates prepare for their exams.
Do certifications cater to different skill levels in cybersecurity?
Yes, cybersecurity certifications cater to different skill levels, from entry-level to advanced. For example:
CompTIAⓇ Security+ is designed for entry-level professionals.
CEH is suitable for intermediate-level practitioners.
CISSP and CISM are aimed at experienced professionals and managers.
OSCP targets those with advanced penetration testing skills.
How do cybersecurity certifications contribute to professional development?
Cybersecurity certifications contribute to professional development by providing formal recognition of expertise, improving job prospects, and often leading to higher salaries. They keep professionals updated with the latest industry trends and best practices, enhance their problem-solving abilities, and expand their professional network through associations with certification bodies and peers.
For more information and resources, you can visit:
CompTIA
EC-Council
ISACA
Offensive Security
Protect Your Organization from Phishing
Explore More Resources
- Article, News
- Article, News
- Article, News
- Article, Blog
Your Trusted Source for Cyber Education
Sign up for ThriveDX's quarterly newsletter to receive information on the latest cybersecurity trends, expert takes, security news, and free resources.